Head & Neck Cancer Screenings
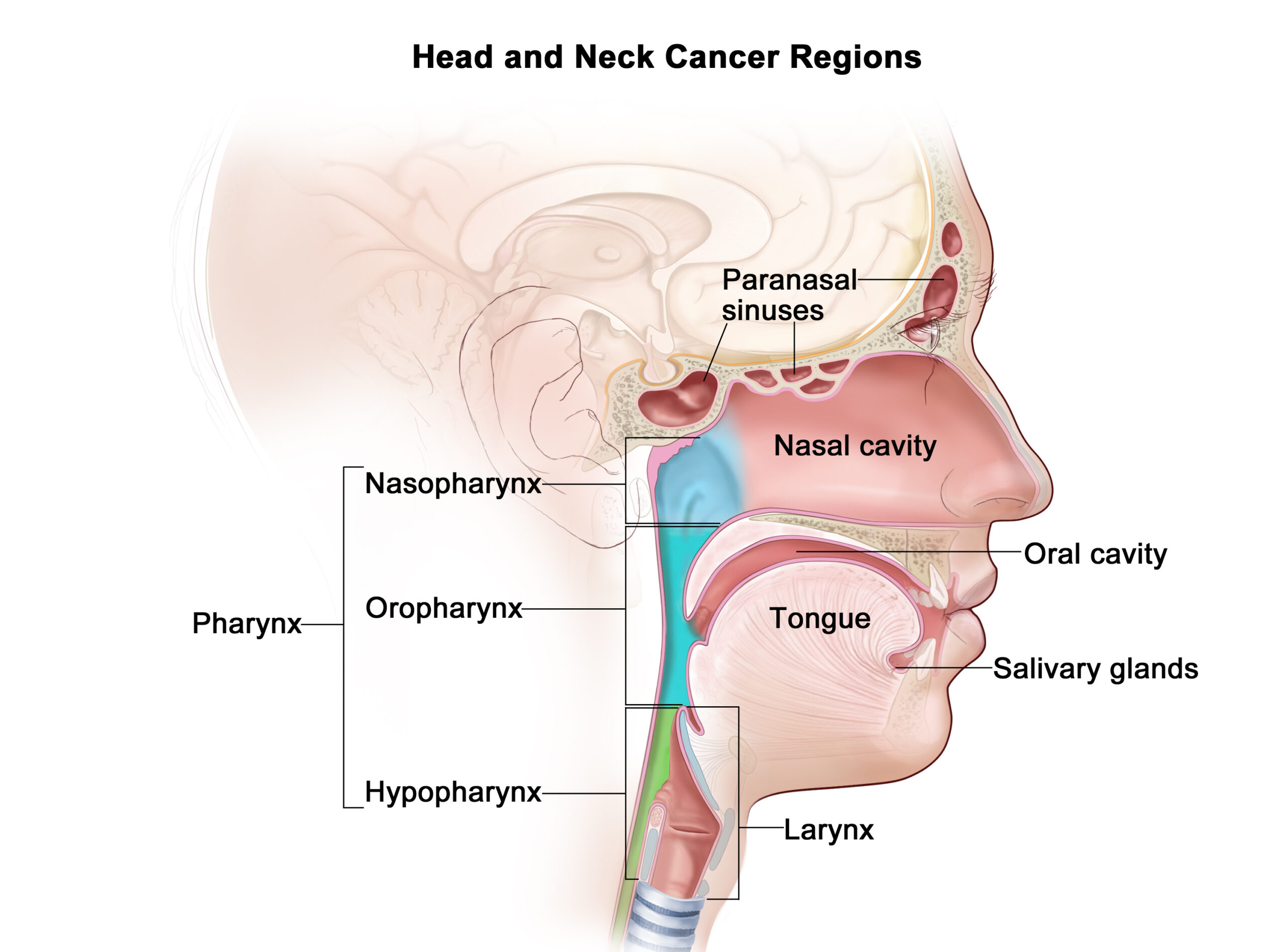
Head and neck cancer screenings involve various methods to detect cancerous or precancerous lesions in the head and neck region. Here are some details about head and neck cancer screenings:
Risk Factors:
- Tobacco and Alcohol Use: Tobacco use (cigarettes, cigars, pipes, chewing tobacco) and heavy alcohol consumption are the primary risk factors for head and neck cancers, particularly oral cavity and laryngeal cancers.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection: Certain strains of HPV, especially HPV-16, are associated with an increased risk of oropharyngeal cancer.
- Occupational Exposure: Exposure to certain occupational hazards such as asbestos, wood dust, nickel, formaldehyde, and radiation can increase the risk of developing head and neck cancers.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Poor oral hygiene and lack of regular dental care can contribute to the development of oral cavity cancers.
Screening Methods:
- Physical Examination: A thorough head and neck examination by a healthcare provider can help detect any suspicious lumps, bumps, or lesions in the oral cavity, throat, neck, and other areas.
- Endoscopy: Endoscopic examinations, such as laryngoscopy and nasopharyngoscopy, involve the use of a thin, flexible tube with a camera to visualize the structures of the throat and larynx.
- Imaging Tests: Imaging studies such as CT scans, MRI scans, and PET scans may be used to evaluate the extent of any suspicious lesions and to determine if cancer has spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes.
- Biopsy: If a suspicious lesion is found during a physical examination or imaging test, a biopsy may be performed to obtain a tissue sample for laboratory analysis. This helps confirm the presence of cancer and determine the type and stage of the disease.
Screening Recommendations:
- No Standard Screening Test: Unlike some other types of cancer (such as breast, cervical, or colorectal cancer), there is currently no standard screening test for head and neck cancers for the general population.
- High-Risk Groups: Screening for head and neck cancers may be recommended for individuals at high risk, such as those with a history of tobacco and alcohol use, HPV infection, or occupational exposure to carcinogens. Regular dental check-ups can also provide an opportunity for oral cancer screening.
- Early Detection: Early detection of head and neck cancers is important for improving treatment outcomes and reducing mortality. Therefore, individuals at high risk should be vigilant about any changes in their oral or throat health and promptly report any concerning symptoms to their healthcare provider.
Preventive Measures:
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking and other forms of tobacco use can significantly reduce the risk of developing head and neck cancers.
- Limiting Alcohol Consumption: Moderating alcohol intake or abstaining from alcohol altogether can also lower the risk of these cancers.
- HPV Vaccination: Vaccination against HPV, particularly for adolescents and young adults, can help prevent HPV-related head and neck cancers.
Regular dental check-ups and discussions with healthcare providers about individual risk factors can help determine if screening for head and neck cancers is appropriate for a person’s specific situation. Early detection and timely intervention are crucial for improving outcomes in individuals diagnosed with head and neck cancers.
